(* Corresponding author; # equal contribution)
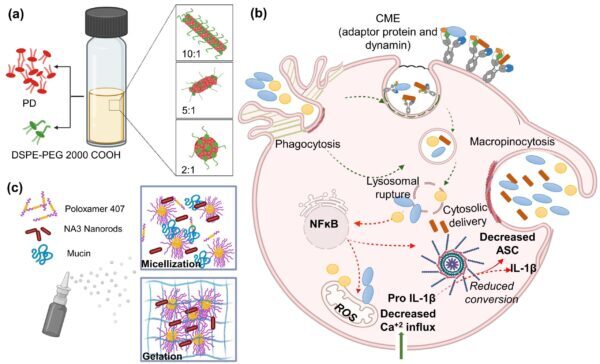
45. Surve D., Fish A., Debnath M., Pinjari A., Lorenzana A., Piya S., Peyton S., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Sprayable Inflammasome-inhibiting Lipid Nanorods in a Polymeric Scaffold for Psoriasis Therapy”, Nature Communications, 2024; 15: 9035. Link
44. Malhotra M., Chotaliya D., Debnath M., Patel R., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Varying the hydrophobic core composition of polymeric nanoparticles affects NLRP3 inflammasome activation, 2024; 12: 4790-4805. Link

43. Nguyen A., Ramesh A., Fish A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Dual-Sensing Nanoreporter for Dynamic and High-throughput Monitoring of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Responses in Tumor-Derived Organoids”, Advanced Functional Materials, 2024; 34(33): 2400393. Link

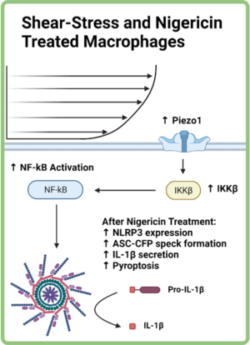
42. Fish A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Flow-Induced Shear Stress Primes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages via Piezo1.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024; 16 (4): 4505–4518. Link
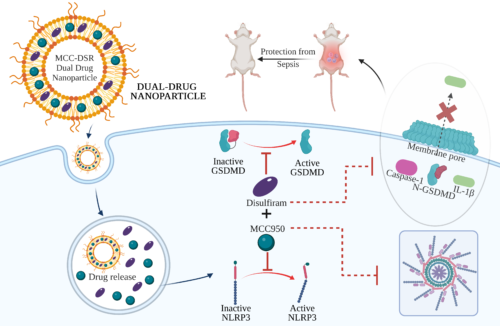
41. Nandi D., Debnath M., Forster J. III, Pandey A., Bharadwaj H., Patel R., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of inflammasome inhibitors provides protection against sepsis.” Nanoscale, 2024; 16: 4678-4690. Link
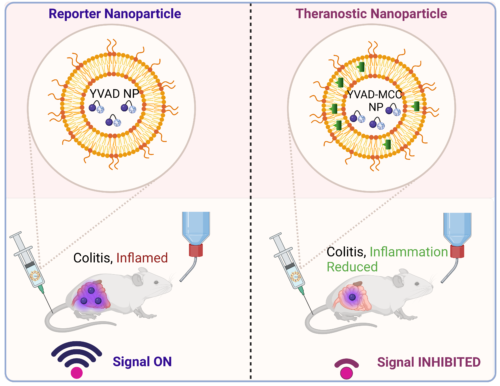
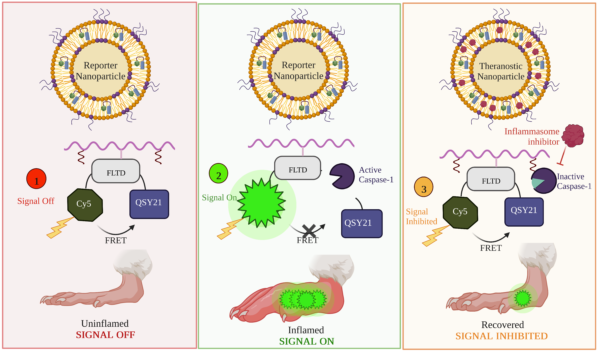
40. Nandi D., Forster J.III, Ramesh A., Nguyen A., Bharadwaj H., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Caspase-1 Responsive Nanoreporter for In Vivo Monitoring of Inflammasome Immunotherapy.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023; 15(48): 55545–55558. Link
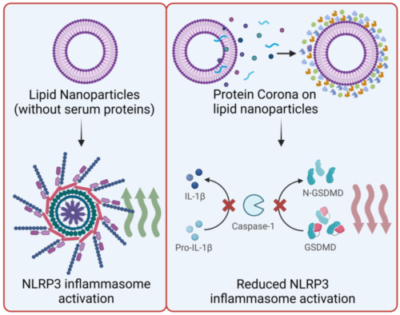
39. Debnath M., Forster J., Ramesh A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Protein Corona formation on Lipid Nanoparticles negatively affects the NLRP3 inflammasome activation.” Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2023; 34(10): 1766–1779. Link
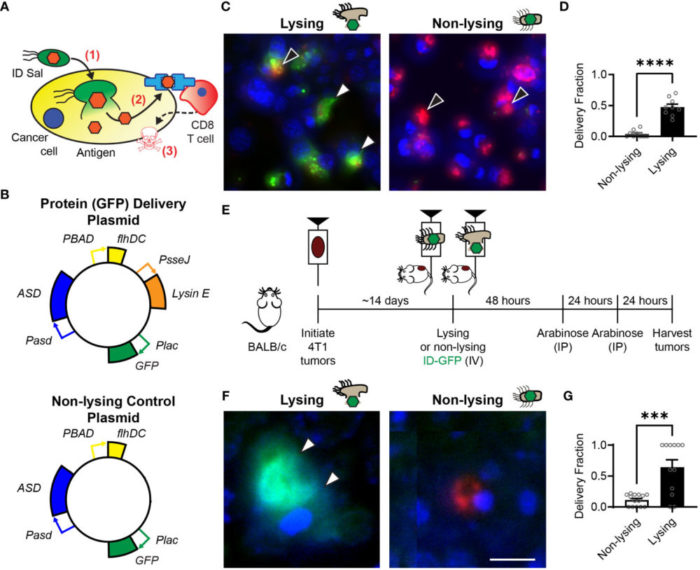
38. Raman V., Howell L., Bloom S., Hall C., Wetherby V., Minter L., Kulkarni A. A., Forbes N.*, “Intracellular Salmonella delivery of an exogenous immunization antigen refocuses CD8 T cells against cancer cells, eliminates pancreatic tumors and forms antitumor immunity.” Front. Immunol., 2023; 14:1228532. Link
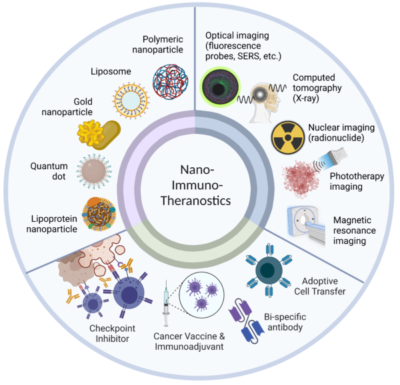
35. Nguyen A., Kumar S., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Nanotheranostic strategies for cancer immunotherapy.” Small Methods, 2022; 6(12):e2200718. Link
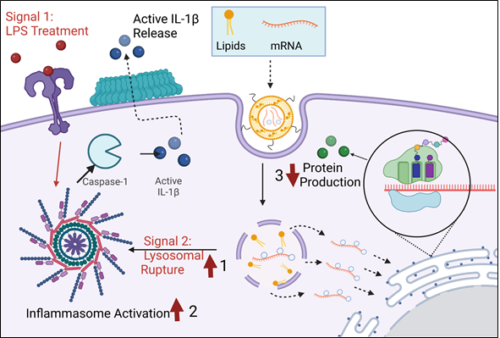
34. Forster J., Nandi D., Kulkarni A. A.*, “mRNA carrying Lipid Nanoparticles that Induce Lysosomal Rupture Activates Inflammasome and Reduces mRNA Transfection Efficiency.” Biomaterials Science, 2022; 10: 5566-5582 . Link
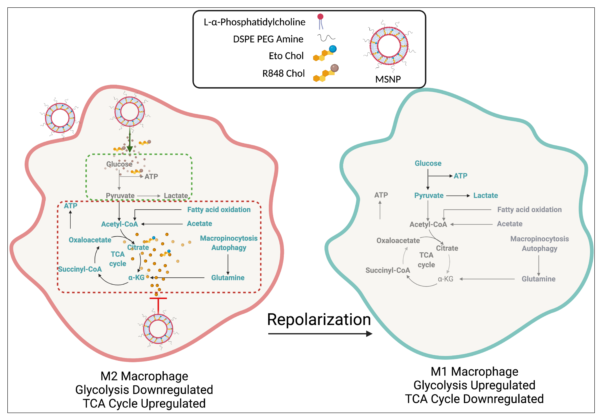
33. Ramesh A., Malik V., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Supramolecular Nanotherapeutics Enable Metabolic reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Inhibit Tumor Growth.” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2022; 110 (8): 1448-1459. Link
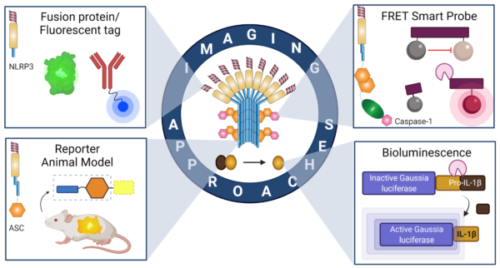
32. Nandi D., Shaheen N., Karuppiah H., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Imaging approaches to monitor inflammasome activation.” Journal of Molecular Biology, 2022; 434(4): 167251. Link
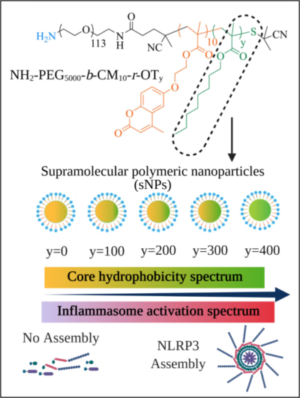
31. Nandi D., Shivrayan M., Gao J., Krishna J., Das R., Liu B., Thayumanavan S.*, Kulkarni A. A.*, “Core Hydrophobicity of Supramolecular Nanoparticles Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021; 13(38): 45300-45314. Link
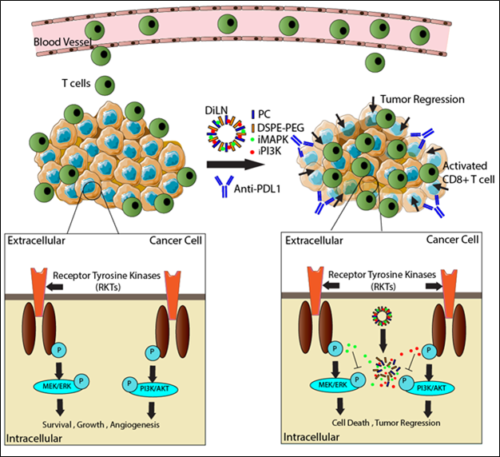
30. Ramesh A., Malik V., Ranjani H., Smith H., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Rational combination of an immune checkpoint inhibitor with CSF1R inhibitor–loaded nanoparticle enhances anticancer efficacy.” Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 2021; 11: 2317-2327. Link
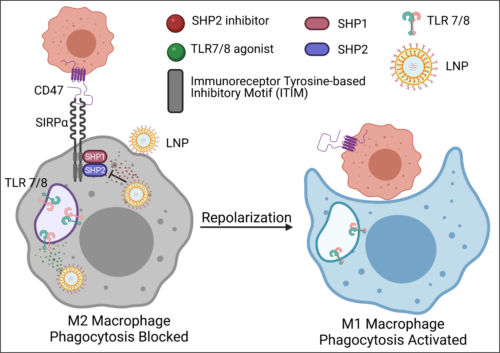
29. Malik V., Ramesh A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “TLR7/8 Agonist and SHP2 Inhibitor Loaded Nanoparticle Enhances Macrophage Immunotherapy Efficacy.” Advanced Therapeutics, 2021; 4(8): 2100086. Link
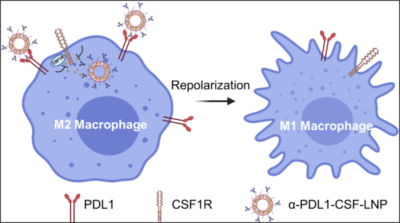
28. Ramesh A., Brouillard A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Supramolecular Nanotherapeutics for Macrophage Immunotherapy.” ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2021; 4, 6: 4653–4666. Link
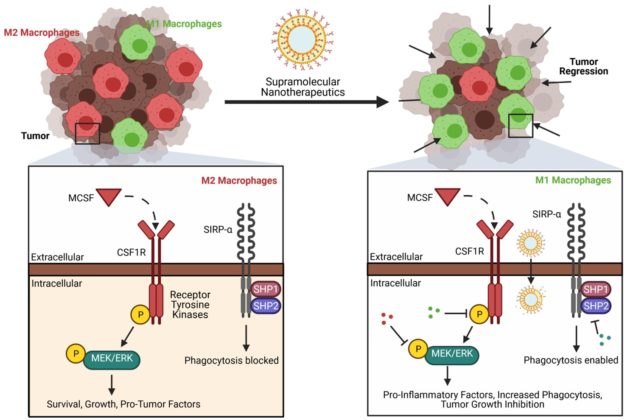
27. Brouillard A.#, Deshpande N.#, Kulkarni A. A.*, “Engineered Multifunctional Nano‐ and Biological Materials for Cancer Immunotherapy.” Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021; 10(6): 2001680. Link
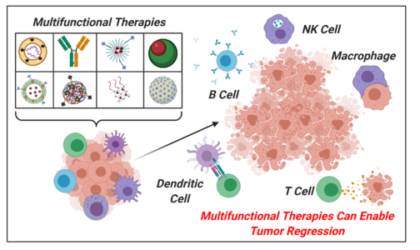
26. Nguyen A., Ramesh A., Kumar S., Nandi D., Brouillard A., Wells A., Pobezinsky L., Osborne B., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Granzyme-B nanoreporter for early monitoring of tumor response to immunotherapy.” Science Advances, 2020; 6(40): eabc2777. Link
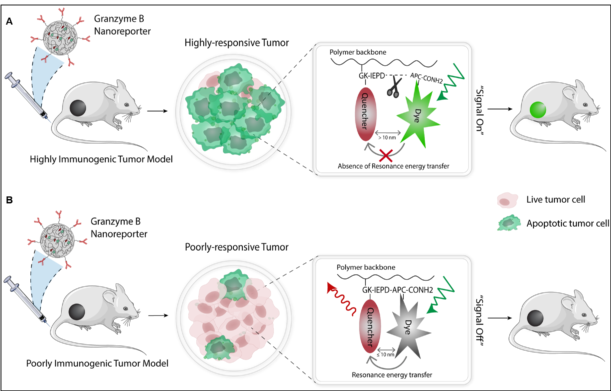
25. Deshpande N., Ramesh A., Nandi D., Nguyen A., Brouillard A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Supramolecular Polysaccharide Nanotheranostics that Inhibit Cancer Cells Growth and Monitor Targeted Therapy Response.” Nanotheranostics, 2020; 4(3): 156-172. Link
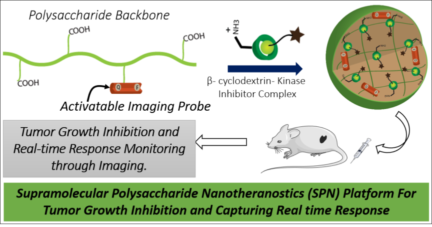
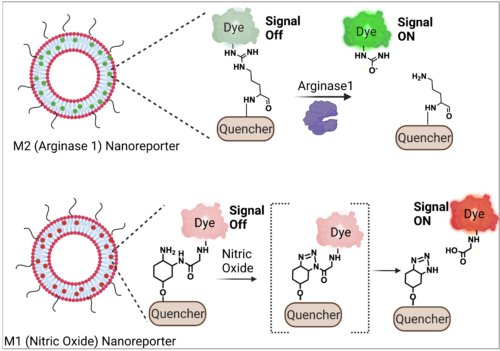
24. Ramesh A., Kumar S., Brouillard A., Nandi D., Kulkarni A. A.*, “A Nitric Oxide (NO) Nanoreporter for Noninvasive Real‐Time Imaging of Macrophage Immunotherapy.” Advanced Materials, 2020; 32 (24): 2000648. Link
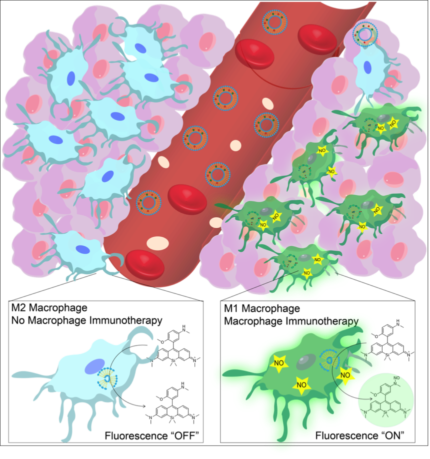
23. Kumar S., Ramesh A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Targeting macrophages: a novel avenue for cancer drug discovery.” Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2020; 15: 561-574. Link
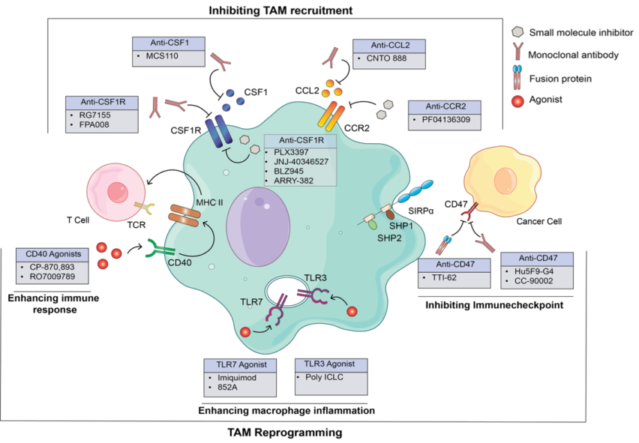
22. Ramesh A., Kumar S., Nguyen A., Brouillard A., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Lipid-based Phagocytosis Nanoenhancer for Macrophage Immunotherapy.” Nanoscale, 2020; 12: 1875-1885. Link
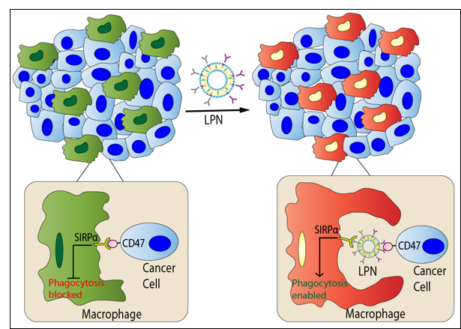
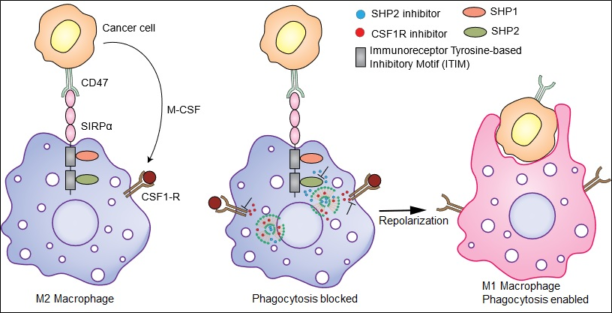
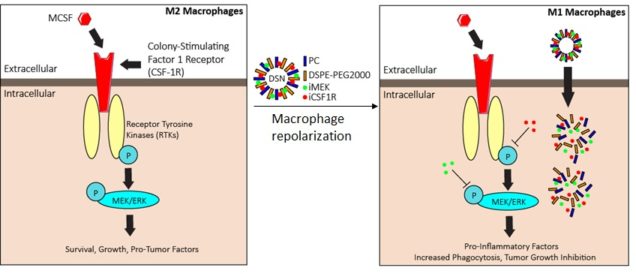
20. Ramesh A.#, Brouillard A.#, Kumar S., Nandi D., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Dual inhibition of CSF1R and MAPK pathways using supramolecular nanoparticles enhances macrophage immunotherapy.” Biomaterials, 2020; 227:119559. Link
19. Ramesh A., Natarajan S. K., Nandi D., Kulkarni A. A.*, “Dual inhibitors-loaded nanotherapeutics that target kinase signaling pathways synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitor.” Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering, 2019; 12:357–373. (Part of 2019 CMBE Young Innovators special issue)
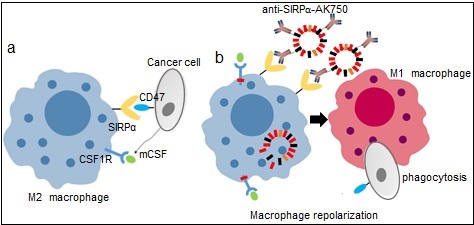
18. Kulkarni A. A.*, Chandrasekar V., Natarajan S., Ramesh A., Pandey P., Nirgud J., Bhatnagar H., Ashok D., Ajay A. and Shiladitya Sengupta*, “A designer self-assembled supramolecule amplifies macrophage immune responses against aggressive cancer.” Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018; 2: 589-599.
Featured in:
Nature Research Highlights: Smart molecule aids natural cancer defences
UMass News : New Cancer Immunotherapy Shows Promise in Early Tests
BBC News: Drug gets body cells to ‘eat and destroy’ cancer
Boston Globe: Brigham and Women’s researchers take another step toward using immune system to fight cancer
Boston Herald: Drug to block weapon used by cancer cells
Medical News Today: ‘Supramolecule’ helps immune cells ‘eat up’ cancer
Science Daily: Eat ’em up: Next-generation therapeutic helps immune cells detect, destroy cancer
The Naked Scientists: Harnessing the immune system to combat cancer
Interview in the Naked Scientists: Can we use the immune system to combat cancer?
Physics World: Supramolecule joins the battle against cancer
Prior to UMass Amherst:
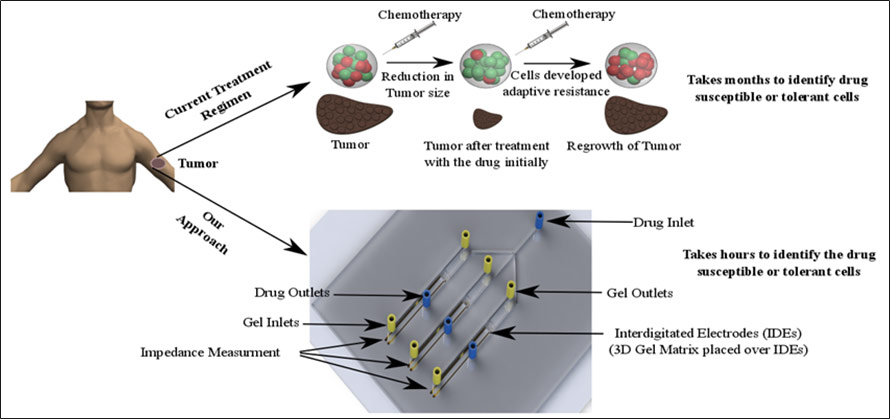
17. Pandya H. J., Dhingra K., Prabhakar D.#, Chandrasekar V.#, Natarajan S. K.#, Vasan A. S., Kulkarni A. A.*, Shafiee H.*, “A microfluidic platform for drug screening in a 3D cancer microenvironment.” Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017; 94: 632-42.
16. Kulkarni A. A.*, Rao P., Natarajan S., Goldman A., Sabbisetti V., Khater Y., Korimerla N., Chandrasekar V., Mashelkar R.*, Sengupta S.*, “Reporter nanoparticle that monitors its anticancer efficacy in real time.”, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016; 1(15): E2104-13.
Featured in (selected from over 140 news articles):
Science News: Cancer killers send signal of success
NDTV.com: Indian Scientists In US Develop Technology For Effective Cancer Treatment
The Scientist: Dying Light Marks the Spot
Medical News Today: New nanoparticle reveals cancer treatment effectiveness in real time
The Economic Times: Indian-origin researchers find a method to watch cancer cell die in real time
Daily Mail: Revolutionary new test could reveal if chemotherapy is working just 8 HOURS after treatment
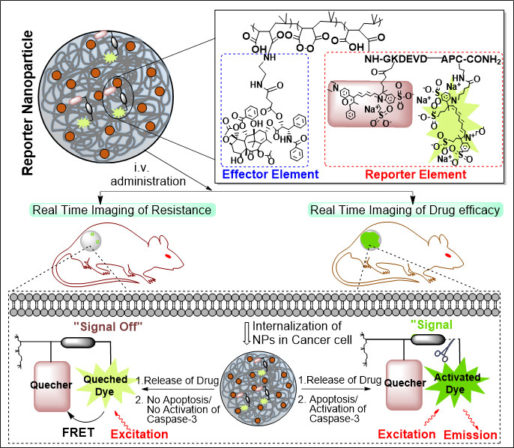
15. Kulkarni A. A., Natarajan S. K., Chandrasekar V., Pandey P, Sengupta S., “Combining immune checkpoint inhibitors and kinase-inhibiting supramolecular therapeutics for enhanced anti-cancer efficacy”, ACS Nano, 2016; 10(10): 9227-42.
(Highlighted in 5 news outlets including Science Daily, Eureka Alert, Nanotechnology Now, Health Medicine Newtork, Phys.org and MedIndia.)
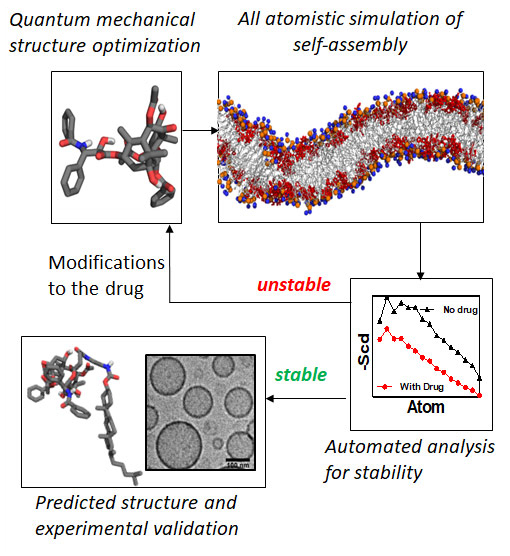
14.Kulkarni A. A., Pandey P, Rao P. S., Mahmoud A., Goldman A., Sabbisetti V., Parcha S., Natarajan S. K., Chandrasekar V., Dinulescu D., Roy S., Sengupta S., “Algorithm for designing nanoscale supramolecular therapeutics with increased anticancer efficacy”, ACS Nano, 2016; 10(9): 8154-68.
Featured in:
ACS Nano Perspective: Facilitating the Clinical Integration of Nanomedicines: The Roles of Theoretical and Computational Scientists
Nanotechnology Now: First multicellular organism inspires the design of better cancer drugs
Health Medicine Network: First multicellular organism inspires the design of better cancer drugs
Medindia: First Multicellular Organism Inspires a Novel Approach for Treating Cancer
PhysOrg: First multicellular organism inspires the design of better cancer drugs
NanoWerk: First multicellular organism inspires the design of better cancer drugs
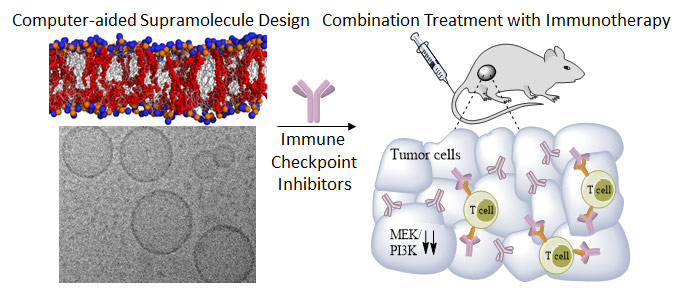
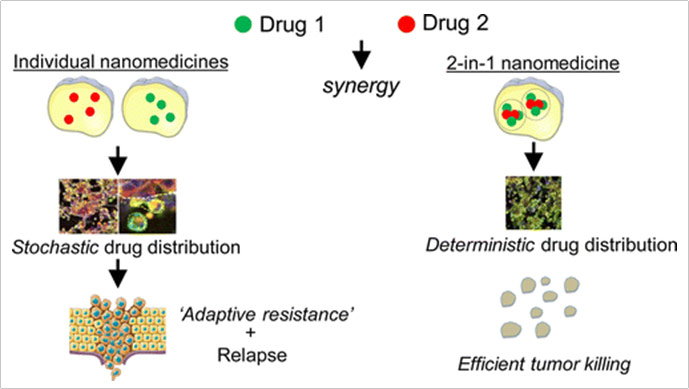
13. Kulkarni A. A. #, Goldman A. #, Kohandel M., Pandey PR., Natarajan S., Ravi S., Sabbisetti S., Sengupta S, “Rationally designed 2-in-1 nanoparticles can overcome adaptive resistance in cancer”, ACS Nano, 2016; 10(6): 5823-5824.
Featured in (selected from over 20 news articles):
NanoWerk: Nanotechnology and math deliver two-in-one punch for cancer therapy resistance
Science News: Nanotechnology, math deliver two-in-one punch for cancer therapy resistance
Scicasts: Researchers Develop New Method that Delivers Two-in-One Punch for Cancer Therapy Resistance
Medindia: Math, Biology, Nanotechnology Deliver 2-in-1 Punch for Cancer Therapy Resistance
ecancer news: Nanotechnology and math ‘deliver two-in-one punch’ for cancer therapy resistance
Health Medicine Network: Researchers engineer revolutionary new approach to combat cancer treatment resistance
GEN News: Resistant Cancer May Lose Tetris-Like Multidrug Challenge
12. Kulkarni A. A.*, Vijaykumar V. E., Natarajan S. K., Sengupta S., Sabbisetti V. S.*, “Sustained inhibition of cMET-VEGFR2 signaling using liposome-mediated delivery increases efficacy and reduces toxicity in kidney cancer”, Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2016; 12(7): 1853-1861.
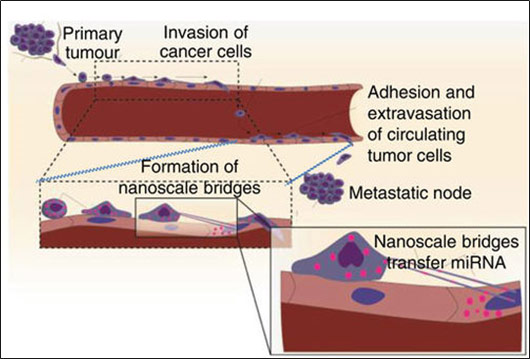
11. Connor Y., Tekleab S., Husain A., Walls C.,…Kulkarni A. A., Zetter B., Dvorak H., Sengupta S., “Physical nanoscale conduits-mediated communication between tumor cells and endothelium modulates endothelial phenotype”, Nature Communications, 2015; 16(6): 8671.
(Highlighted in over 20 news outlets including The Scientist, MIT News, Harvard News, NanoWerk, Health Medicinet, eCancer, The Telegraph and The Tech Times.)
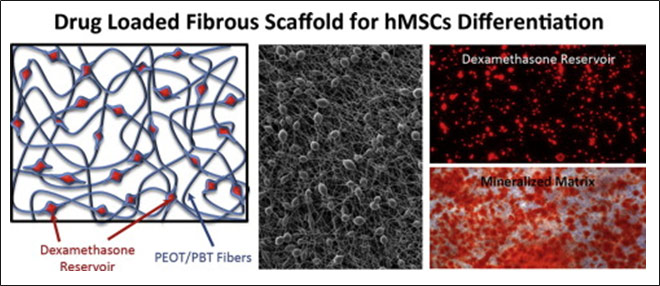
10. Gaharwar A.K. , Mihaila S. M., Kulkarni A. A., Patel A., Di Luca A., Reis R. L., Gomes M. E., van Blitterswijk C., Moroni L., Khademhosseini A., “Amphiphilic beads as depots for sustained drug release integrated into fibrillar scaffolds”, J Control Release, 2014; 187: 66-73.
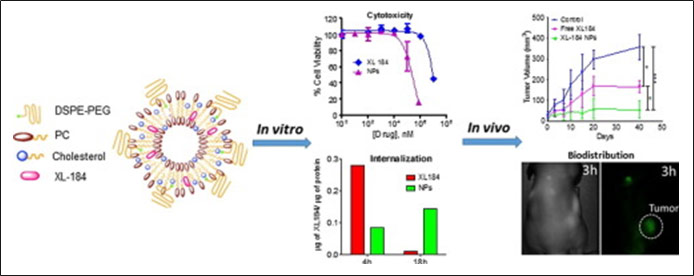
9. Kulkarni A. A.*, Roy B., Rao P. S., Wyant G. A., Mahmoud A., Sengupta S.*, “Supramolecular nanoparticles that target phosphoinositide-3-kinase overcome insulin resistance and exert pronounced antitumor efficacy” Cancer Research, 2013; 73(23): 6987-97.
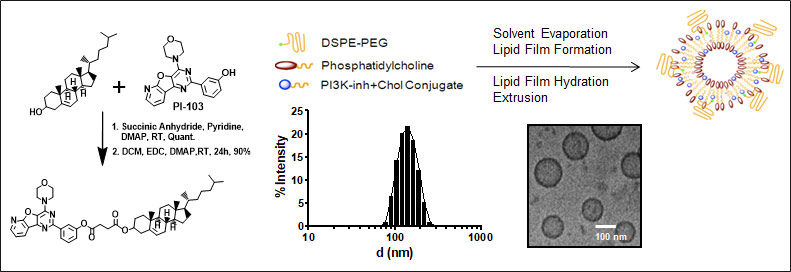
8. Pandey A., Kulkarni A. A., Roy B., Goldman A. J., Sarangi S., Sengupta P., Sengupta S., “Sequential application of a cytotoxic nanoparticle and a PI3K inhibitor enhances antitumor efficacy” Cancer Research, 2014; 74(3): 675-85.
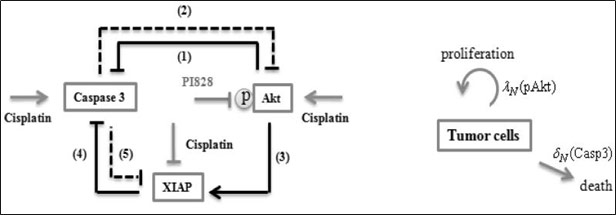
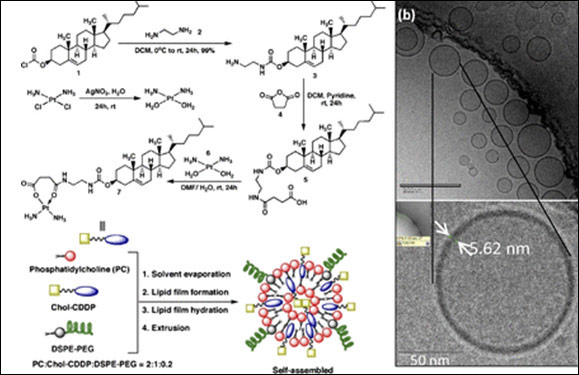
7. Sengupta P., Basu S., Soni S., Pandey A.,…Kulkarni A. A. et.al. “A cholesterol-tethered platinum II-based supramolecular nanoparticle increases antitumor efficacy and reduces nephrotoxicity.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012; 109(28): 11294-11299.
6. Sengupta S., Kulkarni A. A., “Design principles for clinical efficacy of cancer nanomedicine: a look into the basics.” ACS Nano, 2013; 7(4): 2878-82.

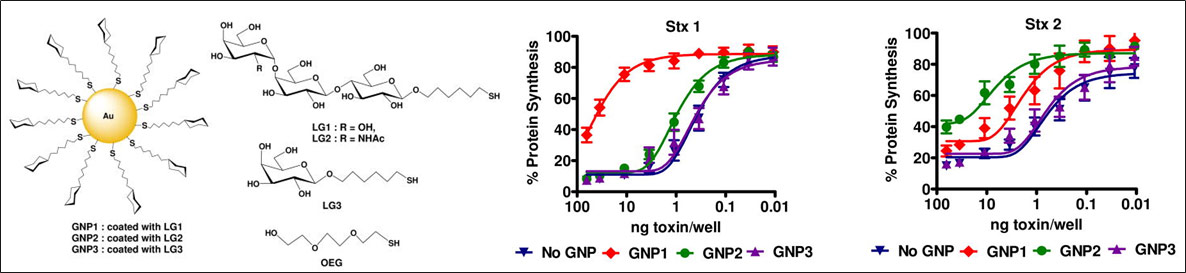
5. Kulkarni A. A., Fuller C., Korman H., Weiss A. A., Iyer S. S., “Glycan encapsulated gold nanoparticles selectively inhibit Shiga toxins 1 and 2.” Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2010; 21(8): 1486-1493.
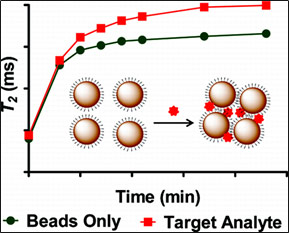
4. Kulkarni A. A., Weiss A. A., Iyer S. S., “Detection of carbohydrate binding proteins using magnetic relaxation switches.” Analytical Chemistry, 2010; 82 (17): 7430-7435.
3. Guo X., Kulkarni A. A., Doepke A. Halsall H. B., Iyer S. S., Heineman W. R., “Carbohydrate-based label-free detection of Escherichia coli ORN 178 using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.” Analytical Chemistry, 2012; 84 (1): 241-246.
2. Flagler M. J., Mahajan S. S., Kulkarni A. A., Weiss A. A. , Iyer S. S., “Comparison of binding platform yields insights into receptor binding differences between Shiga toxins 1 and 2.” Biochemistry, 2010; 49(8): 1649-1657.
1. Kulkarni A. A., Weiss A. A., Iyer S. S., “Glycan based high affinity ligands for toxins and pathogen receptors.” Medicinal Research Reviews, 2010; 30(2): 327-393.